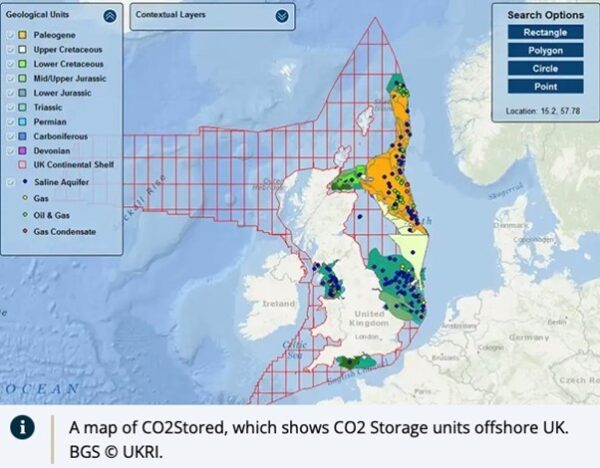
British Geological Survey (BGS) adds more than 60 new carbon dioxide storage units to its national carbon dioxide storage database and delivered the first major update to ‘CO2 Stored’.
The UK Industrial Decarbonisation Research and Innovation Centre (IDRIC) funded research by BGS and Heriot-Watt University (HWU) to update the UK’s national carbon dioxide (CO2) storage database, adding 61 new and updating more than 210 CO2 storage units offshore UK.
CO2 Stored is the UK’s national online evaluation database that identifies the geological storage potential under the UK seabed. Geological storage of CO2 is a key component of industry carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects to permanently reduce release of emissions to the atmosphere.
IDRIC CO2 Stored 2.0 has delivered the first major update of the underpinning data in the UK national database since its population in 2011. Information on oil and gas is confidential for the first five years; this update has added new hydrocarbon field storage data from a 15-year period.
The updated database provides access to 630 potential storage units in the UK, including saline aquifers and depleted oil and gas fields, as well as:
- remapping and updated information for stores in the East Irish Sea Basin
- data from the Government- and industry-supported Peterhead and White Rose CCS and Strategic Storage Appraisal projects
- updates for 205 and addition of 61 hydrocarbon field storage units
The UK is a global leader in provision of online information via its national CO2 storage resource. Data is freely available and gives users access to detailed information on the storage units within the database. It has been the starting point for industry CO2 storage projects, as well as informing Government strategy and providing data for academic research to reduce CO2 emissions in the UK and more widely.
You can read more on the British Geological Survey website here.